Eating Carbs But Still Tired? The Truth About Complex vs Simple Carbs

Table of Contents
Carbohydrates are one of the most talked-about—and misunderstood—parts of modern nutrition. Some diets label them as essential fuel, while others blame them for weight gain and low energy. The confusion often comes from not knowing that carbohydrates are not all the same.
Understanding complex vs simple carbs can help you make smarter food choices, improve your energy levels, and support long-term health without unnecessary restrictions. Instead of avoiding carbs altogether, learning how they work allows you to use them to your advantage.
Let’s break this topic down in a clear, practical, and science-based way.
What Are Carbohydrates and Why Do We Need Them?
Carbohydrates are one of the body’s main sources of energy. When you eat carbs, your body converts them into glucose, which fuels your brain, muscles, and organs.
Carbs also play a role in:
Brain function and focus
Physical performance
Digestive health
Hormonal balance
The key difference lies in how fast different carbs are digested and how they affect blood sugar.
What Are Simple Carbohydrates?
Simple carbohydrates are made up of short sugar chains. Because of their structure, they are broken down very quickly by the body.
Common Foods High in Simple Carbs
Table sugar
Candy and sweets
White bread and baked goods
Sugary cereals
Soft drinks and sweetened beverages
Some natural foods like fruits and dairy also contain simple carbs, but these come with fiber and nutrients, making them a healthier option.
How Simple Carbs Affect the Body
Since simple carbs digest rapidly, they cause a quick rise in blood sugar. This can lead to a short burst of energy followed by a sudden drop.
Frequent consumption of refined simple carbs may result in:
Energy crashes
Increased hunger
Sugar cravings
Difficulty maintaining a healthy weight
This is why simple carbs are often linked to unstable energy levels.
What Are Complex Carbohydrates?
Complex carbohydrates consist of longer chains of sugar molecules. This structure slows digestion and leads to a more gradual release of energy.
Common Sources of Complex Carbs
Whole grains (oats, brown rice, quinoa)
Legumes (beans, lentils, peas)
Vegetables (sweet potatoes, carrots, leafy greens)
Whole wheat products
Seeds and grains
These foods are rich in fiber and essential nutrients.
How Complex Carbs Support Better Health
Complex carbs take longer to digest, which helps maintain steady blood sugar levels. They provide consistent energy instead of sudden spikes and crashes.
Key advantages include:
Long-lasting energy
Better appetite control
Improved digestion
Support for gut health
When looking at complex vs simple carbs, this steady energy release is one of the biggest benefits.
Complex vs Simple Carbs: A Clear Comparison
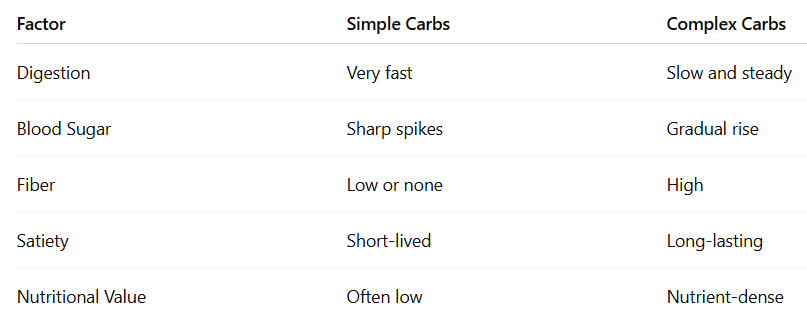
This difference explains why complex carbs are generally recommended for daily meals.
Which Carbs Are Better for Daily Energy?
Simple carbs can be helpful when your body needs quick fuel, such as during intense physical activity or endurance sports. However, for everyday energy, complex carbs are far more reliable.
In the comparison of complex vs simple carbs, complex carbs support sustained focus, productivity, and physical performance throughout the day.
Role of Carbohydrates in Weight Management
Carbs alone do not cause weight gain. The type, portion size, and overall diet quality matter more.
Simple Carbs and Weight Gain
Easy to overeat
Low satiety
Often linked to excess calorie intake
Complex Carbs and Weight Control
High fiber keeps you full longer
Helps reduce unnecessary snacking
Supports a balanced metabolism
Choosing complex carbs can make weight management easier and more sustainable.
Importance of Fiber in Complex Carbs
Fiber is a major reason complex carbs are considered healthier. It slows digestion and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Fiber also supports:
Healthy digestion
Gut bacteria balance
Cholesterol management
Reduced bloating
This makes fiber-rich foods essential in the complex vs simple carbs discussion.
Impact on Blood Sugar and Insulin Health
Simple carbs can cause rapid increases in blood sugar, which may be challenging for people with insulin resistance or diabetes.
Complex carbs help:
Maintain stable glucose levels
Improve insulin sensitivity
Reduce frequent sugar cravings
This makes them a better long-term choice for metabolic health.
Are Simple Carbs Always Unhealthy?
Not necessarily. Whole fruits and dairy contain natural sugars but also provide vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
The real concern is highly processed and refined sugars. Context, quality, and portion size matter more than eliminating simple carbs entirely.
How to Balance Carbs in Your Diet
A healthy diet focuses on balance, not restriction.
Practical Tips:
Choose whole grains instead of refined grains
Combine carbs with protein or healthy fats
Limit sugary drinks and desserts
Watch portion sizes
Understanding complex vs simple carbs allows you to make informed, flexible food choices.
Best Carb Choices Based on Your Goals
For Weight Loss
Oats
Lentils
Vegetables
Brown rice
For Muscle and Strength
Sweet potatoes
Quinoa
Whole grains
For Quick Energy
Fruits
Small amounts of natural sugars
Each type of carb has a purpose when used correctly.
Common Myths About Carbohydrates
Myth: Carbs should be avoided completely
Truth: The right carbs support health and energy
Myth: All simple carbs are bad
Truth: Natural sources can be part of a healthy diet
Myth: Cutting carbs is the only way to lose weight
Truth: Balanced nutrition works better long term
Final Thoughts
The discussion around complex vs simple carbs is not about choosing sides—it’s about understanding how different foods affect your body. Complex carbs provide steady energy, support digestion, and help maintain overall health, while simple carbs can be useful in specific situations when consumed mindfully.
Instead of fearing carbohydrates, focus on quality, balance, and moderation. When chosen wisely, carbs can be one of the most powerful tools for sustained energy and long-term wellness.


